Introduction
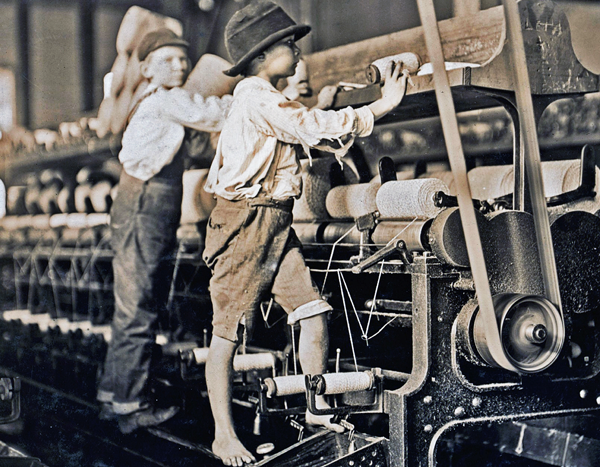
The United States has some of the strictest child labor laws in the world. These laws protect children from being exploited for labor and provide them with an education so they can pursue their dreams later in life. But many people still don’t know what these rights are or how they apply to their lives as employees. So, we’ve put together a list of questions and answers that will help you understand what these laws mean for YOU!
Do federal and state child labor laws differ?
The federal Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) sets the minimum age for employment at 14 years old, but it also allows states to establish their own minimum age requirements. Most states do not have a lower minimum age than the FLSA. However, some states have different hours of work restrictions or exemptions from FLSA for minors under 18 years old. Other state laws may apply in addition to federal child labor laws such as child labor safety standards and requirements related to school attendance.
What are the Child Labor Laws concerning work permits for minors?
While it is technically the responsibility of parents to ensure that their children do not work before their eighteenth birthday, most states have laws in place requiring work permits for minors under 18 years of age. These permits must be signed by a parent or guardian and retained by the employer. This can help prevent minors from working without parental consent.
Some states may require written authorization from a child’s school district before issuing a work permit, while others simply require that children be enrolled in or attend school at least part-time (i.e., six hours per day).
What is the minimum age for employment in the United States?
In the United States, there is a federal minimum age of 14 for most types of employment. The exception is that children under 16 years old may be employed in non-hazardous jobs with parental permission and work permits. In these cases, they must also receive training on how to safely operate certain machinery or equipment.
The minimum age for employment in hazardous jobs is 16 years old (in general). This includes occupations such as construction or heavy industry where the potential danger is higher than other types of work environments. These are often considered “high-risk” positions for young people due to injuries such as burns and falls from heights; however, there are exceptions depending on whether or not you’re working outdoors under direct sunlight/sunlight reflection off water surfaces (like swimming pools) during daylight hours without proper protection from UV rays—this could increase risk levels enough so that all workers have access regardless of their ages! For example:
- Construction work where employees are required wear hard hats, steel toe boots etc., all safety gear needs checked by management prior to starting any project(s) because if one item does not meet OSHA standards then none at all can go forward until corrected!
Are there exceptions to the minimum age requirements of Child Labor Laws?
There are exceptions to the minimum age requirements for employment. These exceptions are listed below:
- Employment in agriculture, including family farms, recreational farms and orchards, where the minor is employed on a seasonal basis an average of not more than 20 hours per week during school years and 40 hours per week when school is not in session;
- Employment in theatrical or entertainment productions; news reporting; advertising sales or fund-raising activities relating to schools or other nonprofit organizations; modeling; work experience investigation; law enforcement agencies/investigations (as long as it does not involve direct contact with offenders); firefighting activities (as long as the minor does not perform any dangerous tasks); lifeguarding at public pools, lakes, rivers and oceans (as long as it does not include diving into water over his head), etc.;
- An exception allowing minors aged 14-15 years old who have completed 8th grade but are otherwise unqualified for general education diploma programs to be employed in non-hazardous occupations outside of non-manufacturing industries where they do not work alone as well as inside retail stores after 6 p.m., provided that these jobs do not interfere with their schooling/class attendance requirement
What are the Child Labor Laws regarding how many hours and when children can work?
The Fair Labor Standards Act sets the minimum age at which a minor may work, and it also prohibits minors from engaging in certain types of work. For all categories, the maximum number of hours that a child can work during a school week is 40. The law also has other requirements regarding what hours can be worked each day and how much time there should be between shifts.
The following information will help you understand whether your business complies with federal child labor laws:
- Minors under 14 years old are not permitted to work at any job except:
- any office or store where only bona fide volunteers are employed;
- on farms owned by their parents;
- at home doing babysitting (but not if their parent(s) receive payment);
- on newspapers that sell ads for more than $10 per year or have more than 25 pages total;
- Minors aged 14 and 15 may do nonagricultural work if they meet one of these three conditions: They must have obtained parental consent, completed an education certificate program in school, or been hired by an employer who employs fewer than 3 workers after first getting permission from a parent who understands the nature of the work his/her child will be doing;
- Minors aged 16 through 17 may perform hazardous occupations such as mining & quarrying jobs; manufacturing jobs like operating power machinery (elevators), meat products processing & food packaging plants); construction jobs related to buildings’ structural integrity (plumbing); automobile repair shops etc.; provided they obtain written consent from parents/guardians AND get trained on how each specific job operates before starting employment at those locations
- Overtime also applies to Children.
When can Child Labor Laws be changed or amended?
The Child Labor Laws can be changed or amended in a number of ways:
- Congress can change the law
- State legislatures can change the law
- Federal and state agencies can change the law
- Courts can change the law
There are some important things to know about child labor laws.
Here are some important things to know about child labor laws:
- Child labor laws generally set a minimum age for employment and prohibit minors from performing dangerous jobs. There are exceptions for certain kinds of work, such as running newspapers or lawnmowers.
- According to a field assistance bulletin issued by the federal Department of Labor (DOL), child labor laws that restrict working hours for 14- and 15-year-olds during the school year still apply even if schools are physically closed due to COVID-19.
Conclusion
Labor laws are intended to protect us, but they can also be confusing and hard to understand. If you are considering hiring a worker under the age of 18, it is important that they are legally allowed to do so. There are also certain limitations on what kind of work can be done by these children and how much time is spent doing it each day.